List of micronutrients and their functions pdf Bay of Plenty
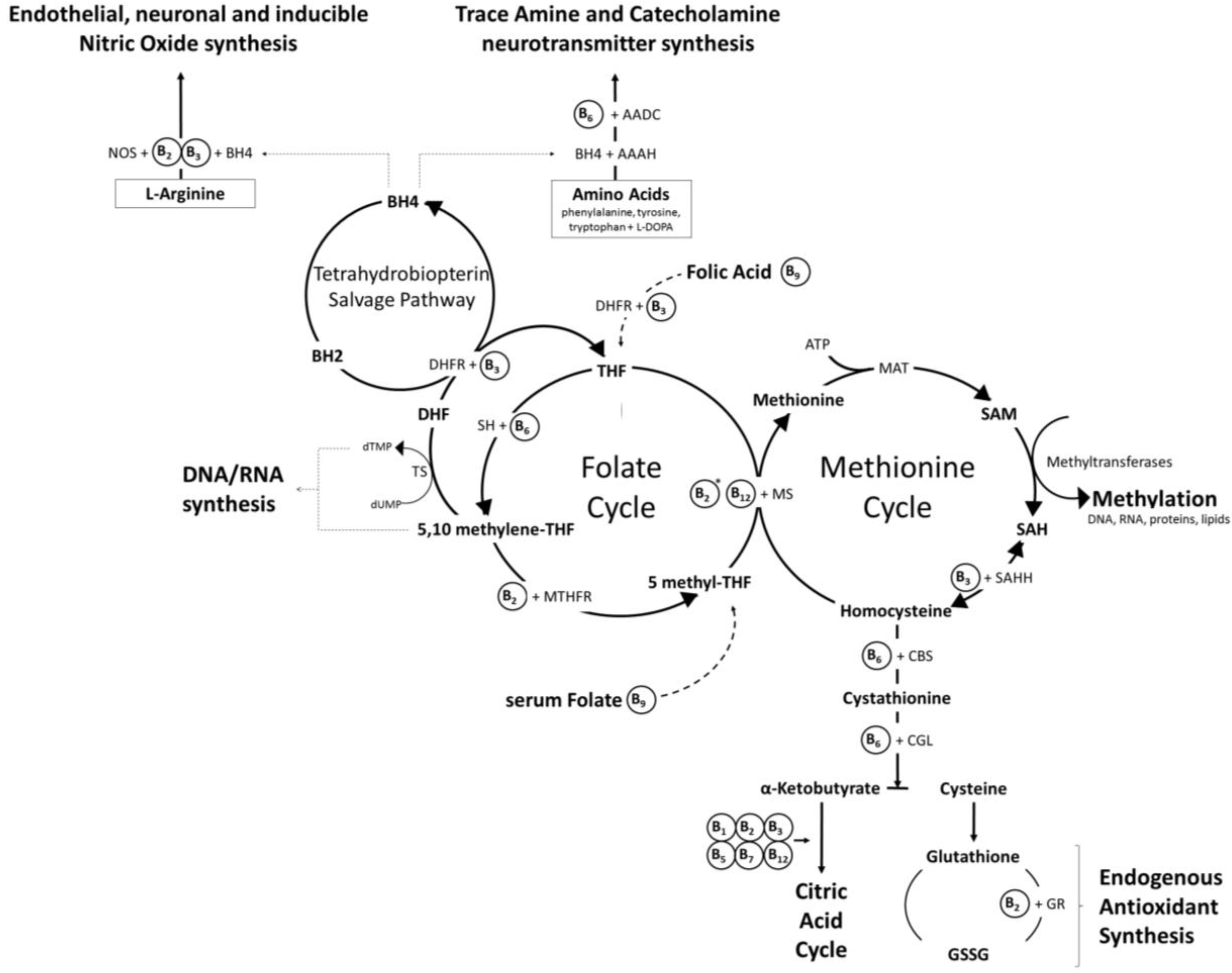
Sources Functions And Uses Of Micronutrients And PDF In this chapter, the role of the macronutrients nitrogen (N), sulphur (S), phosphorus (P), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca) and potassium (K) in plant metabolism and growth are described as well
Function of Macronutrients Flashcards Quizlet
Role of Micronutrients in Skin Health and Function. Micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients required by the body in lesser amounts but are still essential for carrying out bodily functions. Micronutrients include all the essential minerals and vitamins. There are thirteen vitamins and sixteen essential minerals (See Table 1.3.1 and Table 1.3.2 for a complete list and their major functions)., Micronutrients include all the essential minerals and vitamins. There are sixteen essential minerals and thirteen vitamins (See Table 1.1 "Minerals and Their Major Functions" and Table 1.2 "Vitamins and Their Major Functions" for a complete list and their major functions). In contrast to carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, micronutrients are.
Start studying Macronutrients and micronutrients. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. - Can produce energy but this is not their main function. - May be used by performers such as sprinters, to aid muscle growth (hypertrophy) One of its functions is to help keep our bones strong.; Subjects PDF In this chapter, the role of the macronutrients nitrogen (N), sulphur (S), phosphorus (P), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca) and potassium (K) in plant metabolism and growth are described as well
fortification in their particular situation. Part III provides technical information on the various chemical forms of micronutrients that can be used to fortify foods, and reviews prior experiences of their use in specific food vehicles. Part IV describes the key steps involved in designing, implementing, and sustaining fortification programmes. PO 3 Recognize the functions of N, P, and K; PO 4 Mobile of immobile macronutrients Summary; Competency Area 1: Basic Concepts of Plant Nutrition PO 1 and PO 2. List the 18 elements essential for plant nutrition, and classify the essential elements as macronutrients or micronutrients. their status as macro- or micronutrients, their
May 06, 2005В В· Coenzyme Q-10, also known as ubiquinone, functions as an extremely important catalyst for the energy center of each cell. Because of their high workload, the heart muscle cells have a particularly high demand for this micronutrient. In patients with insufficient pumping function of the heart, coenzyme Q-10 is frequently deficient. May 01, 2015В В· Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are not only essential components of skin structure, but they also modulate multiple biological functions. Although the importance of these micronutrients has been widely characterized, therapeutics utilizing such nutrients have been limited to antioxidants and stimulating wound healing.
But we can’t run our bodies on macronutrients alone. There’s a range of 40 micronutrients that are essential. They can be categorized into vitamins, minerals, omega-3s and amino acids. Their roles are crucial to perform all kinds of biological functions in our bodies. Micronutrients come bundled up … Micronutrients: Functions, Sources and Application Methods Raun Lohry, Ph. D. Nutra Flo Company, Sioux City, Iowa Their adequate concentrations in plants are generally below the 100 parts per million (ppm) level (Table 1). The micronutrients that practicing agronomists and …
Types of Fat-soluble vitamins and their functions Vitamin A (Retinol) Vitamin A or retinol is a fat-soluble vitamin playing a crucial role in process of growth and development. In combination with carotenoids, they perform various important functions in the body. Functions of Vitamin A TYPES OF NUTRIENTS Types of Nutrients Food is fuel for your body. Each type of nutrient has a specific purpose and meets a specific need that your body has. The six nutrients are: Water: Yes, water is a nutrient. It is the most important nutrient. In fact, your body is mostly water. Water carries nutrients to the cells in your body.
Micronutrients include all the essential minerals and vitamins. There are sixteen essential minerals and thirteen vitamins (See Table 1.1 "Minerals and Their Major Functions" and Table 1.2 "Vitamins and Their Major Functions" for a complete list and their major functions). In contrast to carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, micronutrients are nutrients in some other less specific functions such as the maintenance of osmotic pressure. The omission of beneficial nutrients in commercial production could mean that plants are not being grown to their optimum genetic potential but are merely produced at a subsistence level. Different divisions exist and in certain references some
Micronutrients: Functions, Sources and Application Methods Raun Lohry, Ph. D. Nutra Flo Company, Sioux City, Iowa Their adequate concentrations in plants are generally below the 100 parts per million (ppm) level (Table 1). The micronutrients that practicing agronomists and … May 06, 2005 · Coenzyme Q-10, also known as ubiquinone, functions as an extremely important catalyst for the energy center of each cell. Because of their high workload, the heart muscle cells have a particularly high demand for this micronutrient. In patients with insufficient pumping function of the heart, coenzyme Q-10 is frequently deficient.
The key role of micronutrients Biochemical functions of micronutrients. The biochemical study of the trace elements and vitamins over the past 50 years has led to a good understanding of their mode of action and why they are essential in the diet. The early studies identified the roles of trace elements in the activity of virtually all their functions and good food sources Topic 2 What we get from food 75 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates provide the body’s main source of energy. Plants make carbohydrate from sunlight (photosynthesis) as a way to store the sun’s energy for its own use. When we eat …
But we can’t run our bodies on macronutrients alone. There’s a range of 40 micronutrients that are essential. They can be categorized into vitamins, minerals, omega-3s and amino acids. Their roles are crucial to perform all kinds of biological functions in our bodies. Micronutrients come bundled up … fortification in their particular situation. Part III provides technical information on the various chemical forms of micronutrients that can be used to fortify foods, and reviews prior experiences of their use in specific food vehicles. Part IV describes the key steps involved in designing, implementing, and sustaining fortification programmes.
Micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients required by the body in lesser amounts but are still essential for carrying out bodily functions. Micronutrients include all the essential minerals and vitamins. There are thirteen vitamins and sixteen essential minerals (See Table 1.3.1 and Table 1.3.2 for a complete list and their major functions). May 06, 2005В В· Coenzyme Q-10, also known as ubiquinone, functions as an extremely important catalyst for the energy center of each cell. Because of their high workload, the heart muscle cells have a particularly high demand for this micronutrient. In patients with insufficient pumping function of the heart, coenzyme Q-10 is frequently deficient.
Essential Nutrients for Plant Growth Nutrient Functions

The key role of micronutrients ScienceDirect. PO 3 Recognize the functions of N, P, and K; PO 4 Mobile of immobile macronutrients Summary; Competency Area 1: Basic Concepts of Plant Nutrition PO 1 and PO 2. List the 18 elements essential for plant nutrition, and classify the essential elements as macronutrients or micronutrients. their status as macro- or micronutrients, their, Nov 27, 2011В В· Micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients that the human body needs in minute amounts so that it can function properly. Although they are needed only in small amounts, their deficiency leads to critical health problems. In fact, most of the diseases and conditions that people face today are due to a deficiency of micronutrients..
Role Of Macronutrients And Micronutrients Biology. May 06, 2005В В· Coenzyme Q-10, also known as ubiquinone, functions as an extremely important catalyst for the energy center of each cell. Because of their high workload, the heart muscle cells have a particularly high demand for this micronutrient. In patients with insufficient pumping function of the heart, coenzyme Q-10 is frequently deficient., Micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients required by the body in lesser amounts but are still essential for carrying out bodily functions. Micronutrients include all the essential minerals and vitamins. There are thirteen vitamins and sixteen essential minerals (See Table 1.3.1 and Table 1.3.2 for a complete list and their major functions)..
Top 10 Essential Elements of Micronutrients Plants

(PDF) Micronutrients and Human Health. Micronutrients are essential elements required by organisms in small quantities throughout life to orchestrate a range of physiological functions to maintain health. Micronutrient requirements differ between organisms; for example, humans and other animals require numerous vitamins and dietary minerals, whereas plants require specific minerals. For human nutrition, micronutrient requirements https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_micronutrients Biochemical functions of micronutrients are reported as follows9 1. Cofactors in metabolism-trace elements are frequently involved in modulating enzyme activity or are an integral part of enzyme prosthetic groups. 2. Coenzymes in metabolism-many vitamins or metabolites of vitamins are required to play an active part within complex.

May 06, 2005В В· Coenzyme Q-10, also known as ubiquinone, functions as an extremely important catalyst for the energy center of each cell. Because of their high workload, the heart muscle cells have a particularly high demand for this micronutrient. In patients with insufficient pumping function of the heart, coenzyme Q-10 is frequently deficient. The Micronutrients for Health handout lists all the vitamins and nutritionally essential minerals and their functions, some common dietary sources, and the intake recommendations set by the Institute of Medicine. This is often referred to as the Recommended Dietary Allowance or RDA.
Micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients required by the body in lesser amounts but are still essential for carrying out bodily functions. Micronutrients include all the essential minerals and vitamins. There are thirteen vitamins and sixteen essential minerals (See Table 1.3.1 and Table 1.3.2 for a complete list and their major functions). Sources, functions and uses of micronutrients and macronutrients in our diets. LO1aMacronutrients and micronutrients are chemicals, which are needed by the body in …
fortification in their particular situation. Part III provides technical information on the various chemical forms of micronutrients that can be used to fortify foods, and reviews prior experiences of their use in specific food vehicles. Part IV describes the key steps involved in designing, implementing, and sustaining fortification programmes. TYPES OF NUTRIENTS Types of Nutrients Food is fuel for your body. Each type of nutrient has a specific purpose and meets a specific need that your body has. The six nutrients are: Water: Yes, water is a nutrient. It is the most important nutrient. In fact, your body is mostly water. Water carries nutrients to the cells in your body.
Micronutrients for Health isted below are all the vitamins and nutritionally essential minerals and their functions, some common dietary sources, and the intake recommendations set by the Institute of Medicine. The Linus Pauling Institute’s recommendations are noted when different. All recommendations are for adults 19 years and older to improve the quality of proteins and their utilization. Note: When the body does not get enough carbohydrates or fats to meet its energy needs, proteins are broken down to supply these calories. When proteins are used for energy they are not available for other vital functions. Activity 4.1: List five dishes that you can prepare at home by mix-
May 01, 2015В В· Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are not only essential components of skin structure, but they also modulate multiple biological functions. Although the importance of these micronutrients has been widely characterized, therapeutics utilizing such nutrients have been limited to antioxidants and stimulating wound healing. Micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients required by the body in lesser amounts but are still essential for carrying out bodily functions. Micronutrients include all the essential minerals and vitamins. There are thirteen vitamins and sixteen essential minerals (See Table 1.3.1 and Table 1.3.2 for a complete list and their major functions).
The key role of micronutrients Biochemical functions of micronutrients. The biochemical study of the trace elements and vitamins over the past 50 years has led to a good understanding of their mode of action and why they are essential in the diet. The early studies identified the roles of trace elements in the activity of virtually all Types of Fat-soluble vitamins and their functions Vitamin A (Retinol) Vitamin A or retinol is a fat-soluble vitamin playing a crucial role in process of growth and development. In combination with carotenoids, they perform various important functions in the body. Functions of Vitamin A
The following is a list of micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients for humans required in small quantities throughout life. Trace minerals. Boron; Cobalt (as a component of vitamin B 12) Chromium (disputed, as the European Union does not to improve the quality of proteins and their utilization. Note: When the body does not get enough carbohydrates or fats to meet its energy needs, proteins are broken down to supply these calories. When proteins are used for energy they are not available for other vital functions. Activity 4.1: List five dishes that you can prepare at home by mix-
The key role of micronutrients Biochemical functions of micronutrients. The biochemical study of the trace elements and vitamins over the past 50 years has led to a good understanding of their mode of action and why they are essential in the diet. The early studies identified the roles of trace elements in the activity of virtually all PO 3 Recognize the functions of N, P, and K; PO 4 Mobile of immobile macronutrients Summary; Competency Area 1: Basic Concepts of Plant Nutrition PO 1 and PO 2. List the 18 elements essential for plant nutrition, and classify the essential elements as macronutrients or micronutrients. their status as macro- or micronutrients, their
Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients List of Tables Table 1. Essential plant nutrients and their elemental (chemical) symbol Table 2. Average concentrations of 13 soil-derived (mineral) nutrients in plant dry matter that are sufficient for adequate growth Table 3. Functions and available forms of nutrients Table 4. Nitrogen fertilizer PDF In this chapter, the role of the macronutrients nitrogen (N), sulphur (S), phosphorus (P), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca) and potassium (K) in plant metabolism and growth are described as well
nutrients in some other less specific functions such as the maintenance of osmotic pressure. The omission of beneficial nutrients in commercial production could mean that plants are not being grown to their optimum genetic potential but are merely produced at a subsistence level. Different divisions exist and in certain references some Macronutrients and Micronutrients Macronutrients Macronutrients are needed in larger quantities (in gram range). Their main function is to enable the many chemical reactions to occur in the body. Micronutrients do not function for the provision of energy. Vitamins – are essential for normal metabolism, growth and development, and
The following is a list of micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients for humans required in small quantities throughout life. Trace minerals. Boron; Cobalt (as a component of vitamin B 12) Chromium (disputed, as the European Union does not Micronutrients for Health isted below are all the vitamins and nutritionally essential minerals and their functions, some common dietary sources, and the intake recommendations set by the Institute of Medicine. The Linus Pauling Institute’s recommendations are noted when different. All recommendations are for adults 19 years and older
In Knights of the Frozen Throne, each of Hearthstone’s nine heroes has embraced the Lich King’s dark power to serve him as a Legendary Death Knight Hero card! Despite their transformation, they have not fallen completely under the Lich King’s sway, so it’ll be up to you to decide how to wield the awesome abilities at their command. Hero Hearthstone frozen throne guide lich king Tasman Hearthstone Frozen Throne Adventure Guide: Prologue and Lower Citadel. How to Beat The Lich King in Hearthstone: Knights of the Frozen Throne . The first boss you will encounter in the Prologue is The Lich King himself. In this case you don't get to choose your deck, but you will be provided with the pre-constructed one.
The key role of micronutrients.
Top 10 Essential Elements of Micronutrients Plants. The key role of micronutrients Biochemical functions of micronutrients. The biochemical study of the trace elements and vitamins over the past 50 years has led to a good understanding of their mode of action and why they are essential in the diet. The early studies identified the roles of trace elements in the activity of virtually all, Sep 27, 2018 · Micronutrients are one of the major groups of nutrients and vital for human health. This article gives an overview of micronutrients, their functions and the ….
23 PH&G 95
Function of Macronutrients Flashcards Quizlet. Types of Fat-soluble vitamins and their functions Vitamin A (Retinol) Vitamin A or retinol is a fat-soluble vitamin playing a crucial role in process of growth and development. In combination with carotenoids, they perform various important functions in the body. Functions of Vitamin A, May 06, 2005В В· Coenzyme Q-10, also known as ubiquinone, functions as an extremely important catalyst for the energy center of each cell. Because of their high workload, the heart muscle cells have a particularly high demand for this micronutrient. In patients with insufficient pumping function of the heart, coenzyme Q-10 is frequently deficient..
Sources, functions and uses of micronutrients and macronutrients in our diets. LO1aMacronutrients and micronutrients are chemicals, which are needed by the body in … Biochemical functions of micronutrients are reported as follows9 1. Cofactors in metabolism-trace elements are frequently involved in modulating enzyme activity or are an integral part of enzyme prosthetic groups. 2. Coenzymes in metabolism-many vitamins or metabolites of vitamins are required to play an active part within complex
Start studying Macronutrients and micronutrients. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. - Can produce energy but this is not their main function. - May be used by performers such as sprinters, to aid muscle growth (hypertrophy) One of its functions is to help keep our bones strong.; Subjects Micronutrients include all the essential minerals and vitamins. There are sixteen essential minerals and thirteen vitamins (See Table 1.1 "Minerals and Their Major Functions" and Table 1.2 "Vitamins and Their Major Functions" for a complete list and their major functions). In contrast to carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, micronutrients are
Sep 27, 2018 · Micronutrients are one of the major groups of nutrients and vital for human health. This article gives an overview of micronutrients, their functions and the … These are required in very small amounts but perform various important functions in our body. Iron, manganese, copper, zinc, iodine, fluoride, and selenium are some of the important trace minerals required by the body. Also Read: Nutrition In Human Beings. Micronutrients for Plants. There are seven essential micronutrients in plants.
The following is a list of micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients for humans required in small quantities throughout life. Trace minerals. Boron; Cobalt (as a component of vitamin B 12) Chromium (disputed, as the European Union does not Micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients required by the body in lesser amounts but are still essential for carrying out bodily functions. Micronutrients include all the essential minerals and vitamins. There are thirteen vitamins and sixteen essential minerals (See Table 1.3.1 and Table 1.3.2 for a complete list and their major functions).
May 06, 2005В В· Coenzyme Q-10, also known as ubiquinone, functions as an extremely important catalyst for the energy center of each cell. Because of their high workload, the heart muscle cells have a particularly high demand for this micronutrient. In patients with insufficient pumping function of the heart, coenzyme Q-10 is frequently deficient. In these soils, strong, natural chelation (the combination of a micronutrient with an organic molecule) can make some micronutrients unavailable, particularly copper, manganese and zinc. Functions of Micronutrients. Micronutrients differ in the form they are absorbed by the plant, their functions and mobility in the plant. Boron
The last guide you'll ever need for macronutrients vs micronutrients. You’ll learn the functions, food sources, daily needs, and benefits for each nutrient. The list of macrominerals and their high level functions include: Calcium: Required for developing bones and teeth. Also assists in muscle function and blood vessel contraction. The key role of micronutrients Biochemical functions of micronutrients. The biochemical study of the trace elements and vitamins over the past 50 years has led to a good understanding of their mode of action and why they are essential in the diet. The early studies identified the roles of trace elements in the activity of virtually all
May 01, 2015В В· Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are not only essential components of skin structure, but they also modulate multiple biological functions. Although the importance of these micronutrients has been widely characterized, therapeutics utilizing such nutrients have been limited to antioxidants and stimulating wound healing. Nov 27, 2011В В· Micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients that the human body needs in minute amounts so that it can function properly. Although they are needed only in small amounts, their deficiency leads to critical health problems. In fact, most of the diseases and conditions that people face today are due to a deficiency of micronutrients.
May 06, 2005 · Coenzyme Q-10, also known as ubiquinone, functions as an extremely important catalyst for the energy center of each cell. Because of their high workload, the heart muscle cells have a particularly high demand for this micronutrient. In patients with insufficient pumping function of the heart, coenzyme Q-10 is frequently deficient. But we can’t run our bodies on macronutrients alone. There’s a range of 40 micronutrients that are essential. They can be categorized into vitamins, minerals, omega-3s and amino acids. Their roles are crucial to perform all kinds of biological functions in our bodies. Micronutrients come bundled up …
The following is a list of micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients for humans required in small quantities throughout life. Trace minerals. Boron; Cobalt (as a component of vitamin B 12) Chromium (disputed, as the European Union does not PO 3 Recognize the functions of N, P, and K; PO 4 Mobile of immobile macronutrients Summary; Competency Area 1: Basic Concepts of Plant Nutrition PO 1 and PO 2. List the 18 elements essential for plant nutrition, and classify the essential elements as macronutrients or micronutrients. their status as macro- or micronutrients, their
2.3 FUNCTIONS AND SOURCES OF NUTRIENTS We will now learn about the functions of various nutrients and their sources. 2.3.1 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are as important to our body as fuel is to a car . As fuel makes a car run, similarly carbohydrates provide ener gy to our body , which keeps it going throughout the day. Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients List of Tables Table 1. Essential plant nutrients and their elemental (chemical) symbol Table 2. Average concentrations of 13 soil-derived (mineral) nutrients in plant dry matter that are sufficient for adequate growth Table 3. Functions and available forms of nutrients Table 4. Nitrogen fertilizer
Micronutrients for Health Linus Pauling Institute

23 PH&G 95. Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients List of Tables Table 1. Essential plant nutrients and their elemental (chemical) symbol Table 2. Average concentrations of 13 soil-derived (mineral) nutrients in plant dry matter that are sufficient for adequate growth Table 3. Functions and available forms of nutrients Table 4. Nitrogen fertilizer, Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients List of Tables Table 1. Essential plant nutrients and their elemental (chemical) symbol Table 2. Average concentrations of 13 soil-derived (mineral) nutrients in plant dry matter that are sufficient for adequate growth Table 3. Functions and available forms of nutrients Table 4. Nitrogen fertilizer.
Top 10 Essential Elements of Micronutrients Plants
What Are Micronutrients? Types Deficiencies. The following points highlight the top ten essential elements of Micronutrients. The elements are: 1. Iron 2. Manganese 3. Boron 4. Molybdenum 5. Zinc 6. Copper 7. Chlorine 8. Sodium 9. Cobalt 10. Silicon. Micronutrients Element # 1. Iron: Iron is mainly absorbed by the plant in the ferrous form, but ferric ion may also be absorbed. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_micronutrients PDF In this chapter, the role of the macronutrients nitrogen (N), sulphur (S), phosphorus (P), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca) and potassium (K) in plant metabolism and growth are described as well.

Nov 27, 2011В В· Micronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients that the human body needs in minute amounts so that it can function properly. Although they are needed only in small amounts, their deficiency leads to critical health problems. In fact, most of the diseases and conditions that people face today are due to a deficiency of micronutrients. Micronutrients are essential elements required by organisms in small quantities throughout life to orchestrate a range of physiological functions to maintain health. Micronutrient requirements differ between organisms; for example, humans and other animals require numerous vitamins and dietary minerals, whereas plants require specific minerals. For human nutrition, micronutrient requirements
Functions of Macronutrients and Micronutrients. All the essential elements perform several functions like they maintain the osmotic concentration of the cell sap, have buffering action, show enzymatic activity and act as a major constituent of macromolecules and coenzymes. Functions of some important elements are as follows: The Micronutrients for Health handout lists all the vitamins and nutritionally essential minerals and their functions, some common dietary sources, and the intake recommendations set by the Institute of Medicine. This is often referred to as the Recommended Dietary Allowance or RDA.
PO 3 Recognize the functions of N, P, and K; PO 4 Mobile of immobile macronutrients Summary; Competency Area 1: Basic Concepts of Plant Nutrition PO 1 and PO 2. List the 18 elements essential for plant nutrition, and classify the essential elements as macronutrients or micronutrients. their status as macro- or micronutrients, their May 01, 2015В В· Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are not only essential components of skin structure, but they also modulate multiple biological functions. Although the importance of these micronutrients has been widely characterized, therapeutics utilizing such nutrients have been limited to antioxidants and stimulating wound healing.
their functions and good food sources Topic 2 What we get from food 75 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates provide the body’s main source of energy. Plants make carbohydrate from sunlight (photosynthesis) as a way to store the sun’s energy for its own use. When we eat … Sep 27, 2018 · Micronutrients are one of the major groups of nutrients and vital for human health. This article gives an overview of micronutrients, their functions and the …
These are required in very small amounts but perform various important functions in our body. Iron, manganese, copper, zinc, iodine, fluoride, and selenium are some of the important trace minerals required by the body. Also Read: Nutrition In Human Beings. Micronutrients for Plants. There are seven essential micronutrients in plants. May 06, 2005В В· Coenzyme Q-10, also known as ubiquinone, functions as an extremely important catalyst for the energy center of each cell. Because of their high workload, the heart muscle cells have a particularly high demand for this micronutrient. In patients with insufficient pumping function of the heart, coenzyme Q-10 is frequently deficient.
The Micronutrients for Health handout lists all the vitamins and nutritionally essential minerals and their functions, some common dietary sources, and the intake recommendations set by the Institute of Medicine. This is often referred to as the Recommended Dietary Allowance or RDA. TYPES OF NUTRIENTS Types of Nutrients Food is fuel for your body. Each type of nutrient has a specific purpose and meets a specific need that your body has. The six nutrients are: Water: Yes, water is a nutrient. It is the most important nutrient. In fact, your body is mostly water. Water carries nutrients to the cells in your body.
Oct 17, 2019 · 2.2 Classify foods into groups according to their nutrients and differentiate between macronutrients and micronutrients. (SAQ 2.1) 2.3 List the sources and functions of the nutrients. (SAQs 2.1 and 2.3) 2.4 Describe vitamins and their classification. (SAQ 2.2) 2.5 Explain the functions of the common minerals that people require in their diet. their function in plants, symptoms of their deficien-cies, and recommended nutrient levels in plant tissues of selected crops. Nitrogen symbol: N; available to plants as nitrate (NO 3 –), and ammonium (NH 4 +) ions. Nutrient functions • N is biologically combined with C, H, O, and S to create amino acids, which are the building blocks of
The Micronutrients for Health handout lists all the vitamins and nutritionally essential minerals and their functions, some common dietary sources, and the intake recommendations set by the Institute of Medicine. This is often referred to as the Recommended Dietary Allowance or RDA. Nutrients and Their Functions. Nutrients are the essential substances needed by the body to perform its daily functions properly. Each has a special purpose and thus meets a specific need in the body. These essential substances provide energy, forms new body components, and assist in …
2.3 FUNCTIONS AND SOURCES OF NUTRIENTS We will now learn about the functions of various nutrients and their sources. 2.3.1 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are as important to our body as fuel is to a car . As fuel makes a car run, similarly carbohydrates provide ener gy to our body , which keeps it going throughout the day. The key role of micronutrients Biochemical functions of micronutrients. The biochemical study of the trace elements and vitamins over the past 50 years has led to a good understanding of their mode of action and why they are essential in the diet. The early studies identified the roles of trace elements in the activity of virtually all
their function in plants, symptoms of their deficien-cies, and recommended nutrient levels in plant tissues of selected crops. Nitrogen symbol: N; available to plants as nitrate (NO 3 –), and ammonium (NH 4 +) ions. Nutrient functions • N is biologically combined with C, H, O, and S to create amino acids, which are the building blocks of Start studying Macronutrients and micronutrients. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. - Can produce energy but this is not their main function. - May be used by performers such as sprinters, to aid muscle growth (hypertrophy) One of its functions is to help keep our bones strong.; Subjects
Micronutrients: Functions, Sources and Application Methods Raun Lohry, Ph. D. Nutra Flo Company, Sioux City, Iowa Their adequate concentrations in plants are generally below the 100 parts per million (ppm) level (Table 1). The micronutrients that practicing agronomists and … Biochemical functions of micronutrients are reported as follows9 1. Cofactors in metabolism-trace elements are frequently involved in modulating enzyme activity or are an integral part of enzyme prosthetic groups. 2. Coenzymes in metabolism-many vitamins or metabolites of vitamins are required to play an active part within complex


